Colon Cancer and Rectal Cancer:
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer, a malignant tumor in the colon or rectum (colon cancer or rectal cancer), is the third most common form of cancer for both men and women in Europe. The risk of developing one of these forms of intestinal cancer increases with age. This risk increases further if this disease runs in the immediate family.
Early stage carcinoma
can be cured by surgery
Minimally invasive or
open surgery
Important for precaution
is the colonoscopy
Symptoms
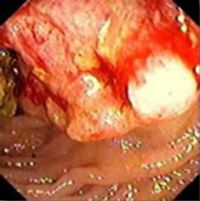
Symptoms include blood in the stool, constipation alternating with diarrhea, pain or weight loss. These symptoms must be investigated immediately, if necessary through a colonoscopy. A tumor as cause of the symptoms can be discovered or eliminated through this simple procedure. This procedure is especially useful for eliminating hemorrhoids or an anal fissure as these cause similar symptoms. Should a suspicious growth be discovered, samples for biopsy can be taken.
Therapy
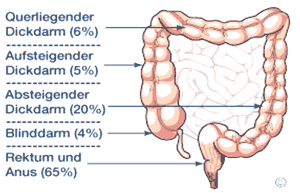
Colorectal therapy depends on which region of the large intestine the tumor is found. There is a major difference between colon tumors and rectal tumors, as colon tumors are more malignant, usually develop from polyps and can develop anywhere in the colon. This kind of tumor is usually accompanied by blood in the stool and can lead to an intestinal obstruction (ileus) in late stages of the disease. Once discovered, there is seldom need for preliminary therapy. Surgical procedures to remove the affected intestinal region usually lead to complete remission of the cancer. The prognosis depends on the stage of development of the cancer, that is if it has spread to the lymph nodes or if metastases occur in other organs.
Testimonial from a patient:
Very nice place, I had nice experience there with operation and the doctor is very careful and taking good care after my surgery.
Source: Google

Surgery
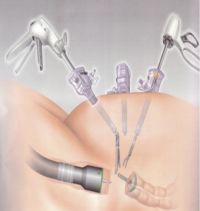
Minimal invasive Laparoscopic colectomy
Minimal invasive laparoscopic colectomy is the surgical removal (called “surgical resection”) of part of the large intestine (colon). A Laparoscopic colectomy is a procedure using the laparoscope during a laparoscopy, which occurs under full anesthetic. In addition, 4 small incisions approximately 5-10 mm long are made near the navel to insert other surgical instruments. The abdominal cavity is expanded with CO2 gas to improve camera perspective and create more operating room. The affected intestinal region with the tumor is cut and removed, and the wounds sutured. If necessary, the surrounding lymph nodes and blood vessels are removed as well, the entire cancerous mass removed from the body through a further small (5-7 cm long) incision and the remaining intestine sutured together.
The minimal invasive surgical procedure heals faster than conventional surgery, and the intestine regenerate faster with less pain. Hospitalization time and at home recovery time are reduced as well. The operation is technically difficult and requires high level of competence and experience by the surgeon.
Prognosis
If the cancer is discovered in early stages, the prognosis for remission is very good. In the earliest stages, surgery can lead to complete recovery. In this case it is necessary to remove all cancerous tissue, including parts of the intestine where the tumor is growing, and blood vessels that supply the tumor with blood, and surrounding lymph vessels and nodes that may also contain cancer cells. If cancer cells are discovered in the lymphatic system, a postoperative chemotherapy will be arranged. This will inhibit further tumor development (metastases) in other organs. If no further cancer cells are discovered, there is no need for chemotherapy. The patient can leave the hospital 8-10 days after the operation, and usually can work again after 3-4 weeks. Dietary restrictions will be recommended until the intestinal tract fully recovers.
Prevention
It is recommended that everyone begin regular check-ups for colorectal cancer at about age 50. This can be done through colonoscopy, a very gentle procedure. During this procedure, any polyps and adenomas (pre-cancerous growths) can be safely removed significantly reducing the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Notice: Preoperative preparation: Please inform your physician if you are taking blood thinning medication such as Aspirin® and Marcumar® as they may lead to complications during surgery. The intestinal tract will be emptied prior to the operation using a laxative or an enema.
Your health is
important to us
Office Hours
Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday: 8:30 – 16:00
Thursday: 8:30 – 18:00
Friday: 8:30 – 13:00
and by appointment
